오늘은 선형자료구조인 연결리스트의 개념과 배열을 통해서 간단히 구현 그리고 마지막으로 연결리스트 기반인 LinkedList에 대해서 알아보는 시간을 가지려고 한다.
ㆍ연결리스트의 개념
연결리스트는 요소가 data와 다음 요소를 가리키는 pointer(참조)로 이뤄져있다.
각 요소를 노드(Node)라고 부르며, 노드는 데이터 필드와 다음 노드에 대한 참조(링크)로 구성.
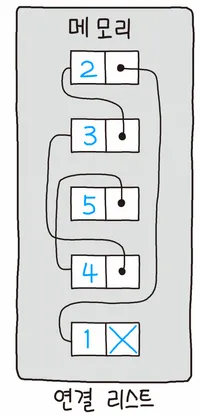
ㆍ연결리스트의 특징
- 비연속적인 메모리 공간
- 각 노드는 독립적인 객체로 메모리에 분산되어 저장 - 가변 크기
- 크기가 동적으로 조절 가능 - 삽입 및 삭제 성능 우수
- 중간에 요소를 추가하거나 삭제할 때 다른 노드들과의 연결만 수정하면 되므로 성능이 우수 - 접근 성능 떨어짐
- 특정 인덱스의 요소에 접근할 때 처음부터 찾아가야 하므로 배열이나 ArrayList보다 느릴 수 있다. - 이중 연결 리스트
- 양방향으로 참조를 가지고 있어 이전 노드로도 쉽게 이동
ㆍ연결리스트의 종류
- 단일 연결 리스트 (Singly Linked List)
- 각 노드가 데이터와 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터로 구성
- 마지막 노드의 다음 노드는 null이다.
- 각 노드는 순차적으로 연결
- 각 노드에 대한 접근은 첫 번째 노드에서 시작하여 다음 노드로 이동하면서 접근 - 이중 연결 리스트 (Doubly Linked List)
- 각 노드가 데이터, 이전 노드를 가리키는 포인터, 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터로 이루어져 있습니다.
- 첫 번째 노드의 이전 노드와 마지막 노드의 다음 노드는 null이다.
- 양방향으로 탐색할 수 있어서 역방향으로도 삽입과 삭제가 용이합니다. - 원형 연결 리스트 (Circular Linked List)
- 마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키는 구조입니다.
- 단일 연결 리스트나 이중 연결 리스트의 마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키면서 원형적인 구조를 가지게 됩니다.
ㆍ단일연결리스트 구현
Node class를 만들어서 간단하게 단일 연결리스트의 추가, 삭제, 찾기, 출력 기능을 만들어보았다.
// 단방향 연결
class NodeA {
int data;
NodeA next;
NodeA(int data, NodeA next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class LinkedListActive {
NodeA head;
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListActive linkedListActive = new LinkedListActive();
linkedListActive.insertLastData(1);
linkedListActive.insertLastData(2);
linkedListActive.insertLastData(3);
linkedListActive.insertLastData(4);
linkedListActive.insertLastData(5);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.insertData(1, 10);
linkedListActive.insertData(3, 20);
linkedListActive.insertData(5, 30);
linkedListActive.insertData(30, 50);
linkedListActive.insertData(20, 60);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.removeLastData();
linkedListActive.removeLastData();
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.removeData(-1);
linkedListActive.removeData(10);
linkedListActive.removeData(50);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.findData(-1);
linkedListActive.findData(1);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
}
LinkedListActive() {
}
LinkedListActive(NodeA nodeA) {
this.head = nodeA;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
if (this.head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void insertData(Integer beforeData, int data) {
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = new NodeA(data, null);
} else if (beforeData == null) {
NodeA cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = new NodeA(data, null);
} else {
NodeA cur = this.head;
NodeA prev = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (beforeData == cur.data) {
if (cur == head) {
this.head = new NodeA(data, cur);
} else {
prev.next = new NodeA(data, cur);
}
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public void insertLastData(int data) {
NodeA nodeA = new NodeA(data, null);
if (head == null) {
head = nodeA;
} else {
NodeA cur = head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = nodeA;
}
}
private void removeData(Integer data) {
if (this.head == null) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
} else if (data == head.data) {
head = head.next;
} else {
NodeA cur = head;
NodeA prev = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (data == cur.data) {
prev.next = cur.next;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public void removeLastData() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
} else if (head.next == null) {
head = null;
} else {
NodeA cur = head;
NodeA prev = cur;
while (cur.next != null) {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
prev.next = null;
}
}
public void findData(int data) {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
} else {
NodeA cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
System.out.println("find Data");
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
System.out.println("Data not find");
}
public void printAllData() {
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("List is empty");
} else {
NodeA cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
ㆍ이중연결리스트 구현
Node class를 만들어서 간단하게 이중연결리스트의 추가, 삭제, 찾기, 출력 기능을 만들어보았다.
// 양방향 연결
class NodeB {
int data;
NodeB prev;
NodeB next;
NodeB(int data, NodeB prev, NodeB next) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
}
public class LinkedList2Active {
NodeB head;
NodeB tail;
LinkedList2Active() {
}
LinkedList2Active(NodeB node) {
head = node;
tail = node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList2Active linkedListActive = new LinkedList2Active(new NodeB(1, null, null));
linkedListActive.insertData(20, 1);
linkedListActive.insertData(3, 20);
linkedListActive.insertData(5, 3);
linkedListActive.insertData(30, 5);
linkedListActive.insertData(100, 30);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.removeData(-1);
linkedListActive.removeData(30);
linkedListActive.removeData(1);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.printReverseAllData();
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void insertData(int data, Integer prevData) {
if (head == null) {
head = new NodeB(data, null, null);
tail = head;
} else if (prevData == null) {
tail.next = new NodeB(data, tail, null);
tail = tail.next;
} else {
NodeB cur = head;
NodeB prev = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (prevData == cur.data) {
if (cur == head) {
head = new NodeB(data, null, head);
head.next.prev = head;
} else {
prev.next = new NodeB(data, prev, cur);
cur.prev = prev.next;
}
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
private void removeData(int data) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
} else {
NodeB cur = head;
NodeB prev = cur;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == head && cur == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else if (cur == head) {
head = head.next;
head.prev = null;
} else if (cur == tail) {
tail = tail.prev;
tail.next = null;
} else {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = prev;
}
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
private void printAllData() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
}
NodeB cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
private void printReverseAllData() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
}
NodeB cur = tail;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.prev;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
ㆍ원형연결리스트 구현
Node class를 만들어서 간단하게 원형연결리스트의 추가, 삭제, 찾기, 출력 기능을 만들어보았다.
//원형연결리스트
class NodeC {
int data;
NodeC prev;
NodeC next;
NodeC(int data, NodeC prev, NodeC next) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class LinkedList3Active {
NodeC head;
NodeC tail;
LinkedList3Active() {
}
LinkedList3Active(NodeC node) {
head = node;
tail = node;
node.prev = head;
node.next = head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList3Active linkedListActive = new LinkedList3Active(new NodeC(1, null, null));
linkedListActive.insertData(20, 1);
linkedListActive.insertData(3, 20);
linkedListActive.insertData(5, 3);
linkedListActive.insertData(30, 5);
linkedListActive.insertData(100, 30);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
linkedListActive.removeData(-1);
linkedListActive.removeData(30);
linkedListActive.removeData(1);
linkedListActive.printAllData();
}
private boolean isEmpty() {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void insertData(int data, Integer prevData) {
NodeC node = new NodeC(data, null, null);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = node;
tail = node;
node.next = node;
node.prev = node;
} else if (prevData == null) {
node.prev = tail;
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
} else {
NodeC cur = head;
NodeC prev = cur;
do {
if (cur.data == prevData) {
if (cur == head) {
node.prev = tail;
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
tail.next = node;
head = node;
} else {
node.prev = prev;
node.next = cur;
cur.prev = node;
prev.next = node;
}
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
} while (cur.next != head);
}
}
private void removeData(int data) {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
} else {
NodeC cur = head;
NodeC prev = cur;
while (cur.next != head) {
if (cur.data == data) {
if (cur == head && cur == tail) {
head = null;
tail = null;
} else if (cur == head) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
head = cur.next;
} else if (cur == tail) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
tail = cur.prev;
} else {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
}
break;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
private void printAllData() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("List is Empty");
} else {
NodeC cur = head;
while (cur.next != head) {
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
ㆍLinkedList의 함수
추가
- add(E element) : 요소를 리스트의 끝에 추가
- addFirst(E element) : 요소를 리스트의 맨 앞에 추가
- addLast(E element) : 요소를 리스트의 끝에 추가, add()와 동일
- addAll(Collection c) : 다른 컬렉션의 모든 요소를 현재 리스트에 추가
삭제
- remove() : 리스트의 첫 번째 요소를 제거
- removeFirst() : 리스트의 첫 번째 요소를 제거
- removeLast() : 리스트의 마지막 요소를 제거
- remove(Object o) : 리스트에서 첫 번째로 나타나는 지정된 요소를 제거
- clear() : 리스트의 모든 요소를 제거
출력
- get(int index) : 지정된 인덱스 위치의 요소를 반환
- size() : 리스트의 요소 개수를 반환
- isEmpty() : 리스트가 비어있는지 여부를 반환
- contains(Object o) : 지정된 요소가 리스트에 포함되어 있는지 여부를 반환
- indexOf(Object o) : 지정된 요소의 인덱스를 반환합니다. 만약 리스트에 존재하지 않으면 -1을 반환합니다.
- toArray() : 리스트의 요소들을 배열로 반환합니다.
'Algorithms > 개념' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 배열과 연결리스트로 Tree 구현 및 기본 개념 정리 (0) | 2024.03.06 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList를 이용한 Deque구현 및 기본 개념 정리 (0) | 2024.03.06 |
| ArrayList를 이용한 Queue구현 및 기본 개념 정리 (0) | 2024.03.06 |
| ArrayList를 이용한 Stack 구현 및 기본 개념 정리 (0) | 2024.03.06 |
| 자바 배열을 활용한 ArrayList 구현 및 기본 개념 정리 (0) | 2024.03.06 |